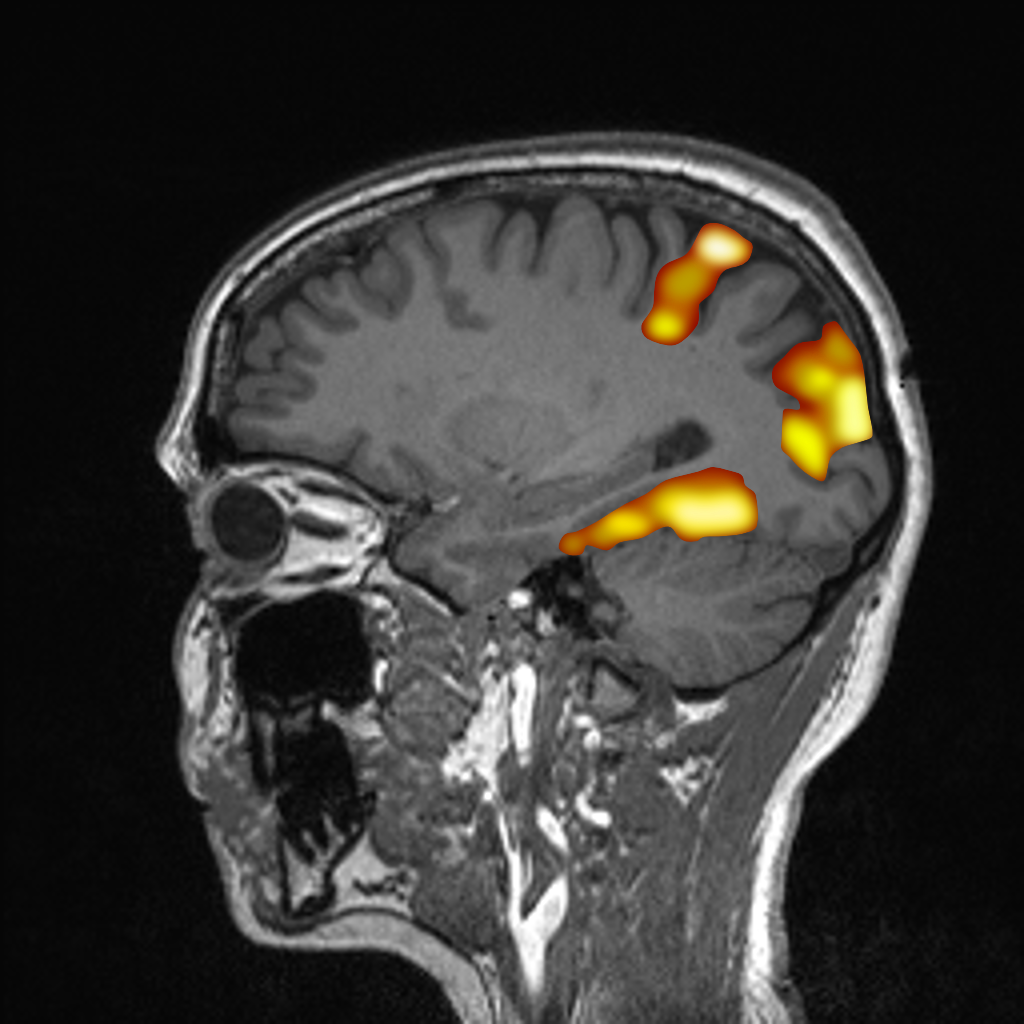
Functional MRI (fMRI) allows imaging of activated brain areas with high spatial resolution. In this process, fMRI detects signal changes due to increased metabolism in the active areas. These changes are based on the different magnetic properties of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood (so-called "blood oxygen level dependent" (BOLD) contrast) and detected by comparing measurements with activation (stimulated state) to measurements without activation (resting state).
Functional brain imaging
Together with our partners from the Clinic and Polyclinic for Psychiatry, Psychosomatics and Psychotherapy at the Universitätsklinikum Würzburg and the Institute of Psychology at the University of Würzburg, studies on virtual reality, emotion processing or anxiety disorders are conducted.
In addition to these projects, novel methods for measuring neuronal activity are being further developed at Fraunhofer EZRT together with scientists from the Institute of Physics at the University of Würzburg. The goal is the direct imaging of currents in the neuronal pathways (neuro electro-magnetic oscillations, NEMO) by means of MRI.
Partner
- Institute of Psychology at the University of Würzburg
- Clinic and Polyclinic for Psychiatry, Psychosomatics and Psychotherapy at the Universitätsklinikum Würzburg)
- Chair of Experimental Physics 5 (Biophysics) at the Physics Institute of the University of Würzburg
Equipment
- 3 Tesla MRI
- 32 channel head coil
- 20 channel head/neck coil
- Standard Bold sequence
- Multiband Bold Sequence for high time resolution
- MRI compatible monitor (in scanner room)
- MRI compatible glasses
- Eye tracking system