What are the key facts about s-net®?
s-net® offers an extremely energy-efficient, wireless solution for networking and localization and belongs to the category of Low Throughput Networks (LTN) with multi-hop communication. The following features distinguish s-net®:
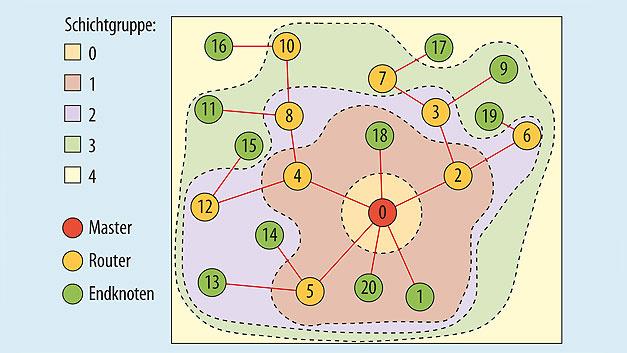
Bidirectional multi-hop communication
Due to the continuous, bidirectional accessibility of all nodes and the forwarding of data via intermediate nodes, the s-net® technology enables the supply of radio nodes via battery. With multi-hop communication, network coverage is not limited to the range of one radio node, but rather can extend to buildings or areas
Dynamic structure and self-organization
s-net® offers an independent and temporal organization of all radio nodes participating in the network. This self-organization occurs decentral at the place of communication and thus supports mobile nodes. The dynamic structure and the self-organization of the meshed network ensure a low configuration and maintenance effort as well as high robustness.
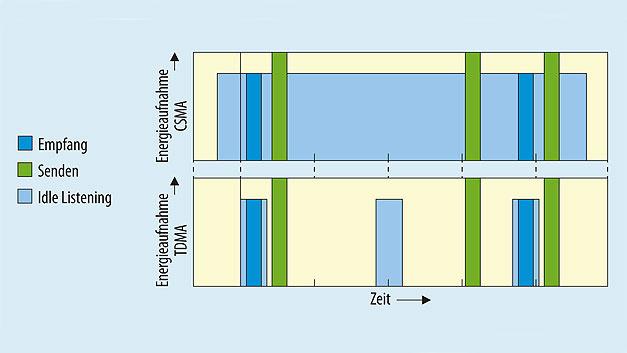
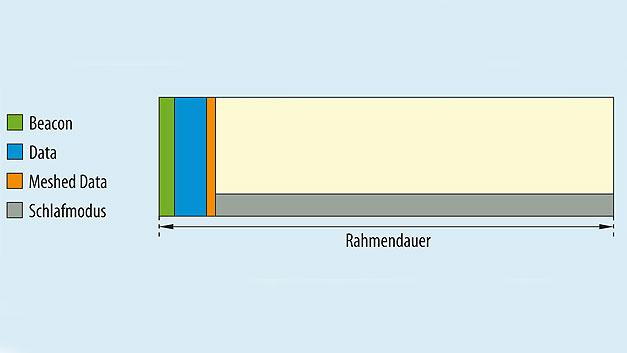
Energy-saving radio communication
s-net® realizes an extremely low power consumption of the radio nodes through time synchronization of the network and time-division multiplex communication. This supports battery operation of all radio nodes. For example, if data is transmitted only at hourly intervals, an average power consumption of less than 50 µA can be achieved with s-net®.